Page 212 - AI Computer 10
P. 212
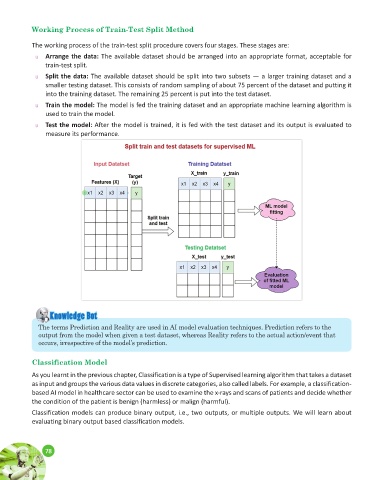
Working Process of Train-Test Split Method
The working process of the train-test split procedure covers four stages. These stages are:
u Arrange the data: The available dataset should be arranged into an appropriate format, acceptable for
train-test split.
u Split the data: The available dataset should be split into two subsets — a larger training dataset and a
smaller testing dataset. This consists of random sampling of about 75 percent of the dataset and putting it
into the training dataset. The remaining 25 percent is put into the test dataset.
u Train the model: The model is fed the training dataset and an appropriate machine learning algorithm is
used to train the model.
u Test the model: After the model is trained, it is fed with the test dataset and its output is evaluated to
measure its performance.
Kno
Knowledge Botwledge Bot
The terms Prediction and Reality are used in AI model evaluation techniques. Prediction refers to the
output from the model when given a test dataset, whereas Reality refers to the actual action/event that
occurs, irrespective of the model’s prediction.
Classification Model
As you learnt in the previous chapter, Classification is a type of Supervised learning algorithm that takes a dataset
as input and groups the various data values in discrete categories, also called labels. For example, a classification-
based AI model in healthcare sector can be used to examine the x-rays and scans of patients and decide whether
the condition of the patient is benign (harmless) or malign (harmful).
Classification models can produce binary output, i.e., two outputs, or multiple outputs. We will learn about
evaluating binary output based classification models.
78
78