Page 341 - AI Computer 10
P. 341
Text Normalisation
Text Normalisation is a technical term used for transforming text into a standard form. It reduces the complexity
of textual data to improve the accuracy and efficiency of later stages, such as sentiment analysis. Normalisation
works on a group of documents, called Corpus.
The various steps used to normalise textual data are:
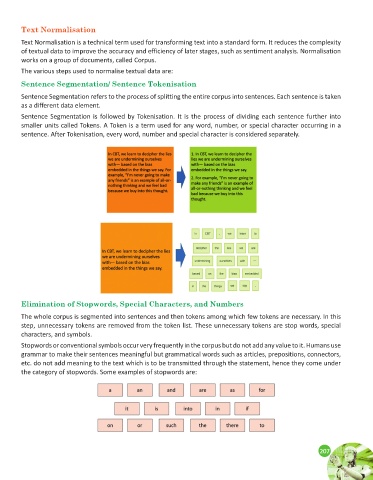
Sentence Segmentation/ Sentence Tokenisation
Sentence Segmentation refers to the process of splitting the entire corpus into sentences. Each sentence is taken
as a different data element.
Sentence Segmentation is followed by Tokenisation. It is the process of dividing each sentence further into
smaller units called Tokens. A Token is a term used for any word, number, or special character occurring in a
sentence. After Tokenisation, every word, number and special character is considered separately.
Elimination of Stopwords, Special Characters, and Numbers
The whole corpus is segmented into sentences and then tokens among which few tokens are necessary. In this
step, unnecessary tokens are removed from the token list. These unnecessary tokens are stop words, special
characters, and symbols.
Stopwords or conventional symbols occur very frequently in the corpus but do not add any value to it. Humans use
grammar to make their sentences meaningful but grammatical words such as articles, prepositions, connectors,
etc. do not add meaning to the text which is to be transmitted through the statement, hence they come under
the category of stopwords. Some examples of stopwords are:
207
207